在知道行為樹以及有限狀態機之前,我寫的軟體或網頁對於程式條件的判斷都是以 if-else、for loop、switch case 撰寫,行為樹只有以前資料探勘有學習過類似的概念。
在政大修習自主行動機器人導論這門課,有幸接觸到行為樹和有限狀態機的理念和實作,打開了一些新世界,所以順便記錄下來分享。
內容目錄
什麼是Behavior Tree?
- 行為樹 (BT) 是一種在自主代理中構建不同任務之間切換的方法,例如:計算機遊戲中的機器人或虛擬實體。
- 在圖 (a) 中可以看到一個 BT 執行拾取 (Pick) 和放置 (Place) 任務的範例。BT 是一種可以有效地建立複雜系統的方法,而這些系統既是模塊化又是可以相互互動的。
- BT 的屬性在許多應用中都非常重要,這讓 BT 從計算機遊戲編程擴展到 AI 和機器人技術的許多分支。
- BT 的優點 (Advantage)
- Modularity
- Hierarchy
- Reusable
- Reactivity
- Expressive
- BT 的缺點 (Disadvantage)
- BT tools are less mature.
- Sometimes a feed-forward execution is just fine.
- Checking all the conditions can be expensive.
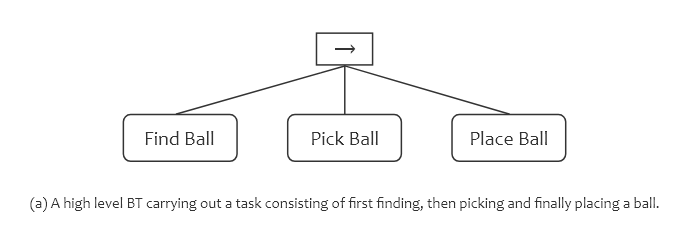
BT 節點類別介紹
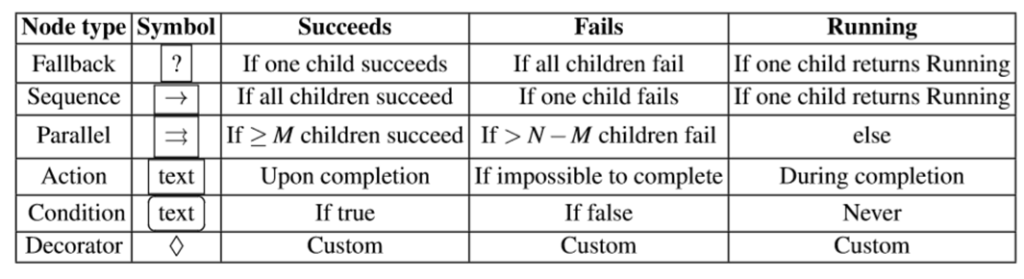
BT 範例
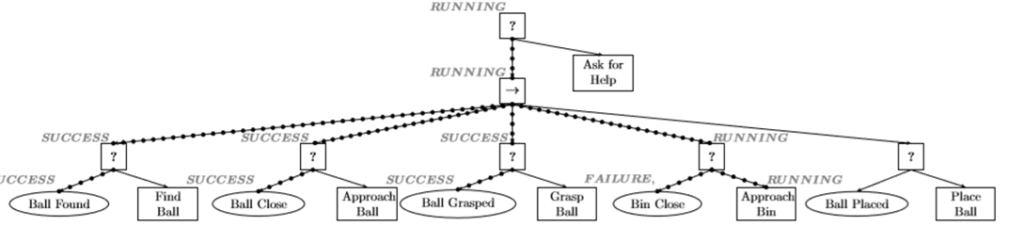
BT 範例1 – Robot放球到籃子中
BT 範例2 – Robot放球到籃子中
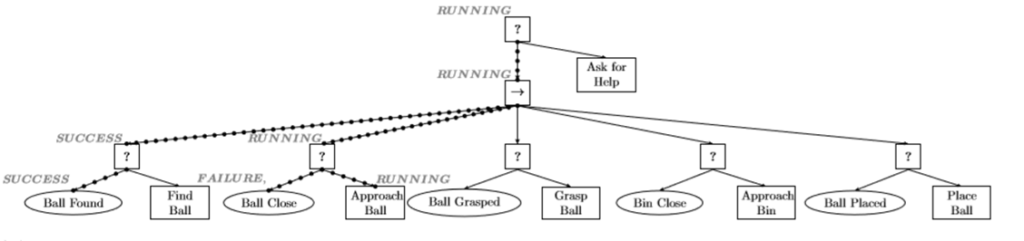
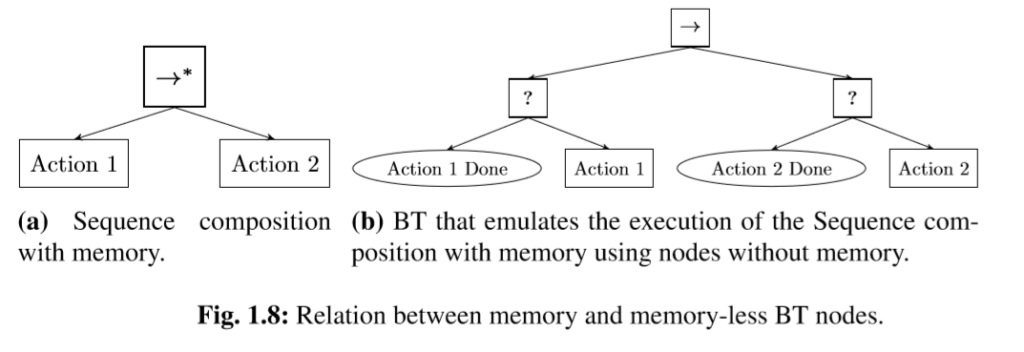
BT Control Flow Nodes with Memory
什麼是FSM?
有限狀態機全名是 Finite-State Machine 維基百科詳解
- 亦可稱為有限狀態自動機 finite-state automaton
- “有限”狀態機,表示在“有限”個狀態中進行狀態之間的轉移和動作
- 優點是:通用結構、直覺且容易理解、容易實作
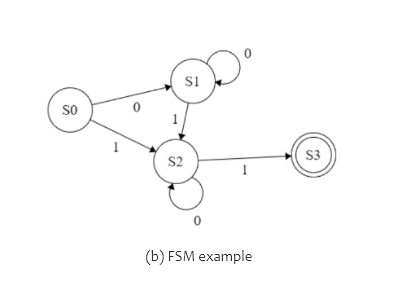
- 舉個簡單的例子 (右圖):判斷輸入字串是否有2個1
- 起始狀態:S0
- 接受(終點)狀態:S3
| 條件 \ 當前狀態 | S0 | S1 | S2 | S3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Input 0 | S1 | S1 | S2 | |
| Input 1 | S2 | S2 | S3 |
FSM的分類
1. 當成接受 / 辨識器 (Σ,S,s0,F…)
- 產生二元輸出(Yes or No)來表示是否被機器接受。當所有輸入被處理後,如果當前狀態是接受狀態,則輸入被接受,否則被拒絕。
- Input:字元 (不使用動作)
- Ex:正規語言
2. 當成變換器 (Σ,S,s0,F…)
- 基於輸入和 / 或狀態產生輸出。
- 應用於控制。
- Ex:電梯門控制
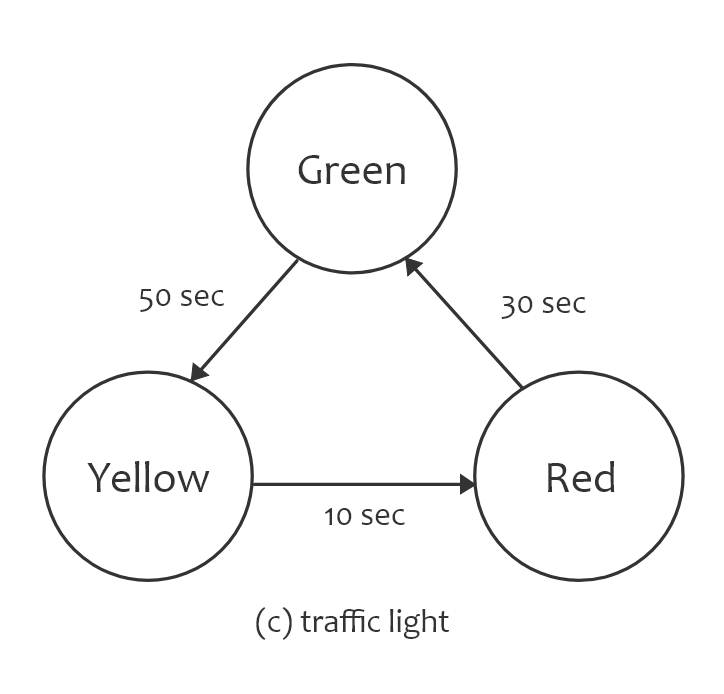
FSM 實作範例 – 紅綠燈跳轉
| 條件 \ 當前狀態 | G | R | Y |
|---|---|---|---|
| 等待時間 10s | R | ||
| 等待時間 30s | G | ||
| 等待時間 50s | Y |
from statemachine import StateMachine, State
class TrafficLightMachine(StateMachine): # 建立狀態機
# 狀態
green = State('Green', initial = True)
yellow = State('Yellow')
red = State('Red')
# 移轉鏈
slowdown = green.to(yellow)
stop = yellow.to(red)
go = red.to(green)
# first
traffic_light = TrafficLightMachine() # 初始化
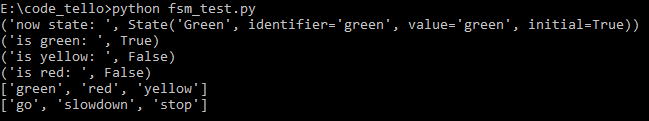
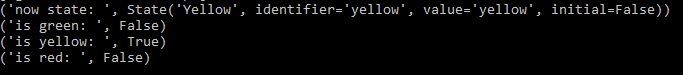
print("now state: ", traffic_light.current_state)
print("is green: ", traffic_light.is_green)
print("is yellow: ", traffic_light.is_yellow)
print("is red: ", traffic_light.is_red)
print( [s.identifier for s in traffic_light.states] )
print( [t.identifier for t in traffic_light.transitions] )
執行結果
在綠燈下做 slowdown
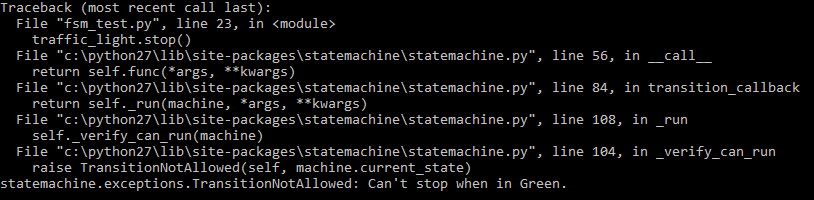
未定義的轉移 → 在綠燈下做stop
進行轉移時執行行為
class TrafficLightMachine(StateMachine): # 建立狀態機
# 狀態
green = State('Green', initial = True)
yellow = State('Yellow')
red = State('Red')
# 移轉鏈
slowdown = green.to(yellow)
stop = yellow.to(red)
go = red.to(green)
# 進行轉移時執行行為
def on_slowdown(self):
print('YELLOW!')
def on_stop(self):
print('RED!')
def on_go(self):
print('GREEN!')
執行結果
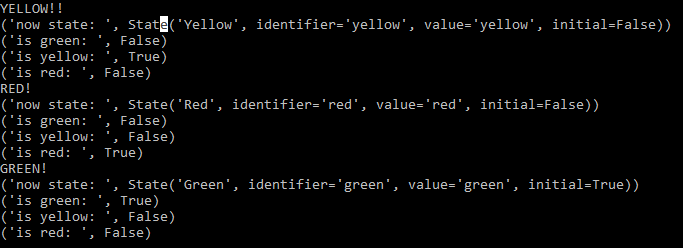
進入狀態時執行動作
class TrafficLightMachine(StateMachine):
green = State('Green', initial = True)
yellow = State('Yellow')
red = State('Red')
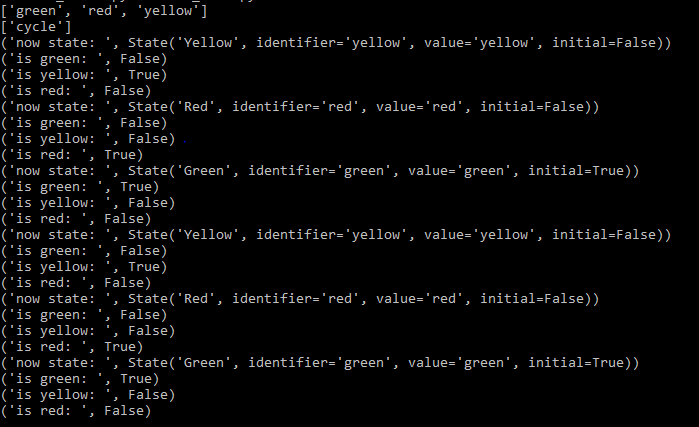
cycle = green.to(yellow) | yellow.to(red) | red.to(green)
#進入狀態時執行動作
def on_enter_green(self):
#self.stop()
time.sleep(50)
def on_enter_yellow(self):
#self.go()
time.sleep(10)
def on_enter_red(self):
#self.slowdown()
time.sleep(30)
def slow(self):
print("now state: ", self.current_state)
print("is green: ", self.is_green)
print("is yellow: ", self.is_yellow)
print("is red: ", self.is_red)
執行結果
行為樹 BT vs. 有限狀態機 FSM
雖然 BT 跟 FSM 都可以做流程控制,不過近幾年的趨勢是什麼呢?
目前主流認為FSM的”單向控制轉移”是個明顯的缺陷。
在FSM的狀態轉換上是單向控制轉移的,但一個好的系統之間是不同的組件之間進行許多轉換。
在FSM如果刪除了一個組件,則經過的每個組件都必須重新修訂,BT則是使用雙向控制傳輸。
因此 BT 在遊戲產業中得到了發展,在NPC的控制結構中增加模組性。關鍵是因為code可以重複使用並且增加功能設計和高效測試。
以前主要是用 FSM,現在 BT 則成為了取代的方案。
(加碼探討) 行為樹 BT vs. 決策樹 DT
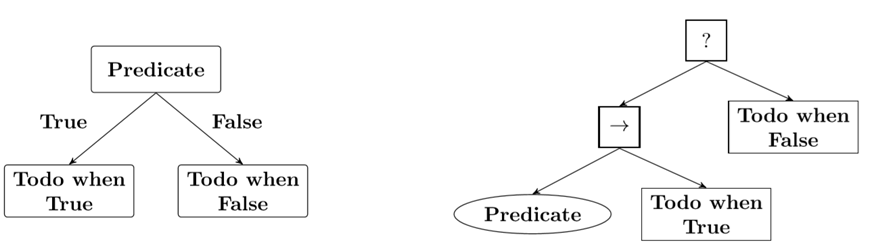
可以看出左邊的決策樹是從“上到下”最後到達端點葉(leaves)的情況,而右側的行為樹是有狀態的,並且會根據當前上下文隨時間從葉子移動到葉子。
這樣看起來,行為樹其實更像狀態機一些。
